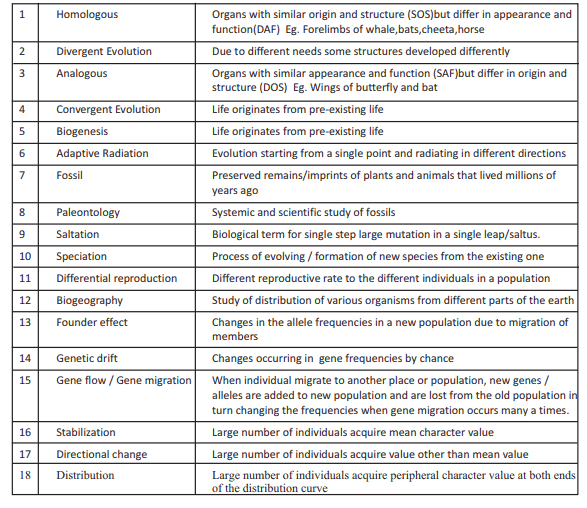
EVENTS IN SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
★Pre-fertilisation
★Fertilisation
★Post-fertilisation
PRE-FERTILISATION
★all the events prior to fusion of gametes are included in it.
★It includes gametogenesis and gamete transfer.
★[A]★ Gametogenesis is the process of formation of male and female gametes.
☆Gametes are haploid cells which may be similar or dissimilar in structure.
★In algae, both gametes are
similar in structure called homogametes (isogametes).
★In higher organism that reproduces
sexually, two morphologically distinct gametes are formed called heterogametes,
 ︎ male gametes are called antherozoid or sperm and
︎ male gametes are called antherozoid or sperm and
 ︎female gametes are called ovum or egg.
︎female gametes are called ovum or egg.
★ heterogametes
In fungi and plants,
★homothallic and monoecious terms are used to denote the bisexual
condition and heterothallic
★dioecious are used for unisexual condition. In flowering
plants,
 ︎the unisexual male flower is staminate, i.e., bearing stamens,
︎the unisexual male flower is staminate, i.e., bearing stamens,
 ︎while the female is
︎while the female is
pistillate or bearing pistils.
★In animals, species which possess both male and female reproductive organs in same individual are called bisexual or hermaphrodites (earthworm, sponges, tapeworm etc.)
★both having either male or female reproductive organs are called unisexual (cockroach,
human).
★Gametes are always haploid( having half set of chromosome ), although organisms may be haploid and diploid.
★Diploid organisms form gametes by meiotic division.
●The organisms
belonging to algae, fungi, and bryophytes have haploid plant body
● pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms and most of animals are diploid ( having double set of
chromosome )
★ In diploid organisms, gamete mother cell (meiocyte) undergoes meiosis in which one set of
chromosome is present in gametes
![]()
![]() OVIPAROUS
OVIPAROUS ![]()