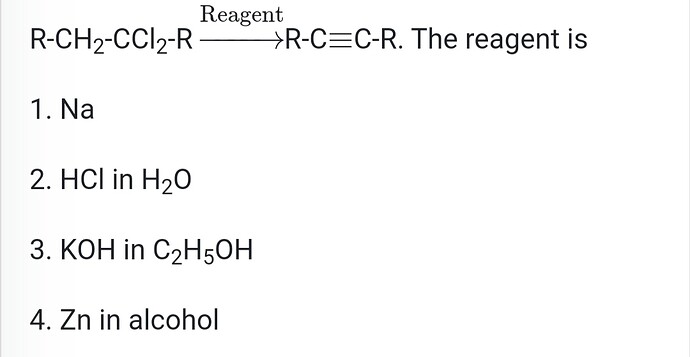- In which year was the Valence bond theory introduced?
(a) 1927
(b) 1920
(c) 1930
(d) 1935
- The oxygen molecule is paramagnetic. It can be explained by
(a) Resonance
(b) Hybridisation
(c) Valence bond theory
(d) Molecular orbital theory
- Bond angle of 120° is found in
(a) PH3
(b) NCl3
(c) ClF3
(d) BCl3
- Which of the following has sp3 hybridisation?
(a) NF3, BF3
(b) SiF4, BeH2
(c) H2S, BF3
(d) NF3, H2O
- Hybridisation of [Ni(CN)4]2- is
(a) dsp2
(b) d2sp2
(c) sp3
(d) d2sp3
- Which of the following is correct for [Mn(CN)6]3-?
(a) dsp2 and square planar
(b) sp3d2 and octahedral
(c) d2sp3 and octahedral
(d) sp3d2 and tetrahedral
- s-orbitals are nondirectional because of
(a) spherical symmetry
(b) their small size
(c) being first orbital
(d) All of the above
- sp2 hybridisation is present in
(a) C2H2
(b) C2H4
(c) BeCl2
(d) C2H6
- The hybridisation and geometry of XeF4 are
(a) sp3d2, square planar
(b) sp3d2, octahedral
(c) sp3d3, triangular planar
(d) sp3d, trigonal bipyramidal
- Which of the following is true for the formation of stable bonds according to valence bond theory?
(a) Greater overlapping between atomic orbitals
(b) Close proximity between two atoms
(c) Pairing of electrons having opposite spins
(d) All of the above
- Ethyne and Ethane can be separated from a mixture by passing it through**
(a) Pyrogallol
(b) Charcoal powder
(c) Concentrated H2SO4
(d) Ammonical Cu2Cl2
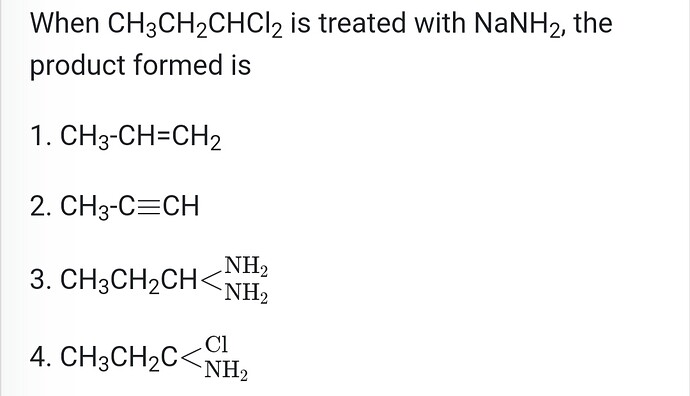
- 1-butyne and 2-butyne can be identified by using which of the following reagents?**
(a) O2
(b) Br2
(c) NaNH2
(d) HCl
- Which of the following is used for welding?
(a) CH4
(b) C2H2
(c) C2H6
(d) C2H4
- The product formed in the reaction of propyne with dilute H2SO4 and HgSO4 is
(a) Propyl hydrogen sulphate
(b) Propanone
(c) Propanal
(d) Propanol
- Polymerisation product of propyne is
(a) Benzene
(b) Ethyl benzene
(c) Propyl benzene
(d) Mesitylene
- The product formed in the reaction of ethyne with dilute H2SO4 and Hg2+ is
(a) Ethyl hydrogen sulphate
(b) Methoxymethane
(c) Ethanal
(d) Ethanol
5.In the ozonolysis reaction, acetylene forms
(a) Formaldehyde
(b) Glycol
(c) Glyoxal, formic acid
(d) None of the above
- Acetylene is oxidised by KMnO4 to form
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Ethyl alcohol
(c) Ethylene glycol
(d) Oxalic acid
- The unit of conductance cannot be expressed in
A. mho
B. (ohm)-1
C. siemens
D. ohm/m
Answer: (d)
- The SI unit of specific resistance is
A. ohm m
B. ohm/m
C. ohm/m2
D. (ohm)-1
Answer: (a)
- The reciprocal of resistivity of a conductor is
A. conductance
B. capacitance
C. conductivity
D. none of these
Answer: (c)
- In order to measure current in a resistance present in a circuit, the ammeter is connected
A. in series
B. in parallel
C. in series or parallel
D. nothing can be decided
Answer: (a)
- Good conductors have many loosely bound
A. atoms
B. protons
C. molecules
D. electrons
Answer: (d)
- The reciprocal of electrical resistance is
A. voltage
B. current
C. conductance
D. none of the above
Answer: (c)
1.The element with the highest conductivity is
A. gold
B. silver
C. copper
D. platinum
Answer: (b)
- As temperature increases electrolytic conduction
A. increases
B. decreases
C. remains unaffected
D. none of the above
Answer: (a)
- The resistance of a conductor varies inversely as
A. length
B. area of cross-section
C. temperature
D. Resistivity
Answer: (b)
- With a rise in temperature, the resistance of semiconductors
A. decreases
B. increases
C. first, increase and then decrease
D. remains constant
Answer: (a)
- When ethyne is passed through a red hot tube, _______ is formed
(a) Cyclohexane
(b) Neoprene
(c) Benzene
(d) Ethane
- The energy released in the form of nuclear radiation in addition to heat and light during nuclear reactions is known as
A. chemical energy
B. nuclear energy
C. heat energy
D. electrical energy
Answer: (b)
- Fireworks release energy in the form of
A. heat
B. sound
C. light
D. all of the above
Answer: (d)
- The energy obtained from electric cells and batteries as a result of a chemical reaction is called
A. chemical energy
B. nuclear energy
C. heat energy
D. electrical energy
Answer: (a)
- As the rain falls the potential energy changes to
A. thermal energy
B. chemical energy
C. kinetic energy
D. nuclear energy
Answer: (c)
- The energy coming directly from magma called
A. mechanical energy
B. geothermal energy
C. heat energy
D. electrical energy
Answer: (b)
- In the process of rubbing hands, mechanical energy is converted into
A. sound energy
B. electrical energy
C. thermal energy
D. heat energy
Answer: (c)
- When a body vibrates, it produces
A. sound
B. water
C. heat
D. electricity
Answer: (a)
- In the exothermic reaction, the enthalpy of reaction is always
A. zero
B. positive
C. negative
D. none of these
Answer: (c)
- The heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a substance by 1o is called
A. specific heat
B. molar heat capacity
C. water equivalent
D. specific gravity
Answer: (b)
5.The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a body through 1oC is called its
A. molar heat
B. specific heat
C. entropy
D. thermal capacity
Answer: (b)
- The variations in enthalpy that can not be detected per calorimeter can be detected with the aid of
A. Newton’s law
B. Hess’s law
C. Krebs law
D. Ohm’s law
Answer: (b)
- The energy required to sever a given covalent bond is named
A. bond energy
B. bond enthalpy
C. bond dissociation energy
D. all of above
Answer: (d)
- Changes in enthalpy in an exothermic reaction is
A. positive
B. negative
C. constant
D. neutral
Answer: (b)
- The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can not be
A. created only
B. destroyed only
C. converted
D. created and destroyed
Answer: (d)
- Hess’s law states that a chemical reaction is independent of the route by which chemical reactions takes place while keeping the same
A. initial conditions only
B. final conditions only
C. mid-conditions
D. initial and final conditions
Answer: (d)
- The standard enthalpy change of neutralization involves the reaction of an acid with an alkali to form 1 mol of
A. water
B. oxygen
C. nitrogen
D. anhydrous salt
Answer: (a)
- The change in the energy between a chemical reaction and the surroundings at constant temperature is called
A. enthalpy change
B. enthalpy
C. enthalpy profile
D. dynamic enthalpy
Answer: (a)
- To initiate a reaction the minimum energy which is required to break bonds is called
A. bond energy
B. activation energy
C. breaking energy
D. ionization energy
Answer: (a)
- The standard condition for enthalpy changes are
A. the pressure of 100 kPa
B. temperature 298K
C. normal physical state
D. all of above
Answer: (d)
- The application of law of thermodynamics to the enthalpy change was done by
A. Newton
B. Hess’s
C. Lewis
D. Sophocles
Answer: (b)
- Bleaching powders chemical name is
A. calcium hypo oxychloride
B. calcium oxychloride
C. calcium chloride
D calcium chloro oxide
Answer: (b)
- The ratio of the water molecule in plaster of paris and gypsum is
A. 3:1
B. 1:3
C. 1:4
D. 4:3
Answer: (c)
- Baking powder is
A. sodium carbonate + sodium tartaric
B. sodium bicarbonate + sodium tartaric
C. sodium carbonate + tartaric acid
D. sodium carbonate + sodium benzoate
Answer: (b)
- Gastric juice contains HCl which is one example of
A. inorganic acid
B. organic acid
C. soft organic acid
D. strong inorganic acid
Answer: (a)
- When milk of magnesia reacts with acetic acid it produces
A. basic salts
B. acidic salts
C. neutral salt
D. complex salt
Answer: (c)
- Which of the following phenomena will occur when a small amount of acid is added to water?
A. dilution
B. neutralisation
C. salt formation
D. ionization
Answer: (a, d)
- Brine is used for industrial production of
A. NaOH
B. KOH
C. bleaching powder
D. none of the above
Answer: (a)
- When base reacts with the non-metal oxide
A. it neutralizes each other
B. it creates fire
C. it produces acidic salts
D. it produces basic salts
Answer: (a)
- Corrosive effect on the skin is caused by
A. acids
B. bases
C. water
D. mercury
Answer: (a, b)
- The acid used for the manufacture of fertilizers and explosives is
A. nitric acid
B. sulfuric acid
C. phosphoric acid
D. hydrochloric acid
Answer: (a)
- In what manner will increase of pressure affect the following equation
C(s) + H2O → CO(g) + H2(g)
A. shift in the reverse direction
B. shift in the forward direction
C. increase in the yield of hydrogen
D. no effect
Answer: (a)
- The equilibrium between water and its vapour in an open vessel
A. can be achieved
B. depends upon pressure
C. cannot be achieved
D. depends upon temperature
Answer: (c)
- When a catalyst is added to a reversible reaction in equilibrium state the value of the equilibrium constant
A. increases
B. decreases
C. does not change
D. becomes zero
Answer: (c)
- A vessel at equilibrium contains SO3, SO2 and O2, now some helium gas is added so that total pressure increases while temperature and volume remain constant. According to Le Chatelier Principle the dissociation of SO32-
A. decreases
B. remain constant
C. increases
D. change unpredictably
Answer: (b)
- The chemical equilibrium of a reversible reaction is not influenced by
A. temperature
B. pressure
C. catalyst
D. concentration
Answer: (c)
- Le Chatelier Principle is applicable to
A. heterogeneous reaction
B. homogeneous reaction
C. irreversible reaction
D. system in equilibrium
Answer: (d)
- The equilibrium constant of a reaction is 300. If the volume of reaction flask is tripled the equilibrium constant is
A. 300
B. 600
C. 900
D. 100
Answer: (a)
- For a reversible reaction the concentration of the reactants are doubled, then the equilibrium constant
A. becomes one-fourth
B. is doubled
C. is halved
D. remains the same
Answer: (d)
- The role of a catalyst in a reversible reaction is to
A. alter the equilibrium constant of the reaction
B. increase the rate of the forward reaction
C. allow the equilibrium to be achieved quickly
D. decrease the rate of backward reaction
Answer: (c)
5.In which of the following cases does the reaction go farthest to completion?
A. K = 1
B. K = 10
C. K = 10-2
D. K = 102
Answer: (d)
- Could BF3 acidity be clarified using one of the following concepts?
A. Arrhenius concept
B. Bronsted Lowry concept
C. Lewis concept
D. Bronsted Lowry as well as Lewis concept
Answer: (c)
- What will be the value of pH of 0.01 mol dm-3 CH3COOH (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5)?
A. 3.4
B. 3.6
C. 3.9
D. 3.0
Answer: (a)
- Which of the following options will be correct for the stage of half completion of the reaction A ⇌ B?
A. Go = 0
B. Go > 0
C. Go < 0
D. Go = – RT ln 2
Answer: (a)
- What should be the correct order of the gas, acetone and ether vapour concentration at 30℃.Considering that water has a maximum boiling point among these compounds, and that ether has a minimum boiling point?
A. water > ether > acetone
B. water < acetone < ether
C. ether < acetone < water
D. acetone < ether < water
Answer: (b)
- What is the pH of the resulting solution when equal volumes of 0.1M NaOH and 0.01M HCl are mixed?
A. 7.0
B. 1.04
C. 12.05
D. 2.0
Answer: (c)
- Which one of the following species cannot act as both Bronsted acid and base?
A. H2O
B. HCO3–
C. HSO4–
D. NH2–
Answer: (d)
- Which of the following salts will give the highest pH in the water?
A. KCl
B. NaCl
C. Na2CO3
D. CuSO4
Answer: (c)
- The aqueous solution of NH4Cl is
A. alkaline
B. acidic
C. neutral
D. none of these
Answer: (b)
- For acidic solution
A. pH = 7
B. pH < 7
C. pH > 7
D. None of these
Answer: (b)
5.The oxidation number of Cr in K2CrO4 is
A. +6
B. -6
C. +8
D. -8
Answer: (a)
- Equimolar solutions of the following compounds are prepared separately in water. Which will have the lowest pH value?
A. BeCl2
B. SrCl2
C. CaCl2
D. MgCl2
Answer: (a)
- Addition of which chemical will decrease the hydrogen ion concentration of an acetic acid solution?
A. NH4Cl
B. Al2(SO4)3
C. AgNO3
D. NaCN
Answer: (d)
- In some solutions, the concentration of H3O+ remains constant even when small amounts of strong acid or strong base are added to them. These solutions are known as
A. ideal solution
B. colloidal solution
C. true solution
D. buffer solution
Answer: (d)
- All compounds are in equilibrium in a reversible reaction. If reactants are doubled in concentration the equilibrium constant would be
A. reduced to half its original value
B. reduced to one-fourth of its original value
C. doubled
D. constant
Answer: (d)
- The solubility of Fe(OH)3 would be maximum in
A. 0.1M NaOH
B. 0.1M HCl
C. 0.01M KOH
D. 0.1M H2SO4
Answer: (d)
- Which of the following sulphides has the largest value of Ksp?
A. CuS
B. CdS
C. PbS
D. ZnS
Answer: (d)
- According to Le Chatelier’s principle adding heat to a solid and liquid in equilibrium will cause the
A. amount of solid to decrease
B. amount of liquid to decrease
C. temperature to rise
D. temperature to fall
Answer: (a)
- 0.1M solution of which of the substances will be basic?
A. sodium borate
B. ammonium chloride
C. calcium nitrate
D. sodium sulphate
Answer: (a)
- At a certain temperature 2HI ⥨ H2 + I2 only 50% HI is dissociated at equilibrium. The equilibrium constant is
A. 0.25
B. 1.0
C. 3.0
D. 0.6
Answer: (a)
- Which has the highest degree of ionization?
A. 0.1M NH3
B. 0.001M NH3
C. 0.1M NH3
D. 0.0001M NH3
Answer: (d)
- The structure of hydrogen peroxide is
A. Planar
B. Spherical
C. Linear
D. Non-planar
Answer: (d)
- Fenton’s reagent is
A. Zn + HCl
B. Sn + HCl
C. FeSO4 + H2O2
D. None
Answer: (c)
- Hydrogen peroxide is
A. oxidising agent
B. reducing agent
C. oxidising as well as reducing
D. None
Answer: (c)
- In the disproportionation Hydrogen peroxide, forming H2O and O2 its equivalent weight is
A. 8.5
B. 17
C. 34
D. 68
Answer: (c)
- The gram equivalent weight of H2O2 as a reductant is
A. 34
B. 68
C. 18
D. 17
Answer: (d)
- H2O2 cannot oxidise
A. Na2SO3
B. O3
C. PbS
D. KI/HCl
Answer: (b)
- Which of the following contains peroxide linkage?
A. SO2
B. MnO2
C. NO2
D. BaO2
Answer: (d)
- Which of the following statement is false
A. H2O2 is oxidising
B. H2O2 is reducing
C. H2O2 is basic
D. H2O2 is acidic
Answer: (c)
- Which of the following gives hydrogen peroxide on electrolysis?
A. H2SO4
B. H2O
C. HCl
D. None of the above
Answer: (a)
- Acidified potassium permanganate is dropped over sodium peroxide taken in a round bottom flask at room temperature, the vigorous reaction takes place to produce
A. hydrogen peroxide
B. a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen
C. a colourless gas hydrogen
D. a colourless gas dioxygen
Answer: (d)